Assessment of a patient with hypoglycemia will most likely reveal: – Assessment of a patient with hypoglycemia will most likely reveal a constellation of physical signs, laboratory abnormalities, and historical clues that point to a deficiency in blood glucose levels. This article delves into the characteristic manifestations of hypoglycemia, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals in accurately diagnosing and managing this condition.
The clinical presentation of hypoglycemia can vary depending on the severity of the episode, ranging from mild symptoms to life-threatening complications. Understanding the typical findings associated with hypoglycemia is crucial for prompt recognition and appropriate intervention.
Assessment of a Patient with Hypoglycemia: Assessment Of A Patient With Hypoglycemia Will Most Likely Reveal:
Hypoglycemia is a condition characterized by abnormally low blood glucose levels. It can occur in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as well as in other conditions such as sepsis, liver disease, and certain medications.
Physical Examination
Common physical signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia:* Confusion
- Diaphoresis
- Hunger
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Palpitations
- Shaking
- Slurred speech
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
- Tremors
- Weakness
Vital signs that may be affected by hypoglycemia:* Blood pressure: May be low or elevated
Heart rate
May be rapid or slow
Respiratory rate
May be rapid or shallow
Temperature
May be normal or lowNeurological manifestations that can occur with severe hypoglycemia:* Seizures
- Coma
- Death
Laboratory Findings
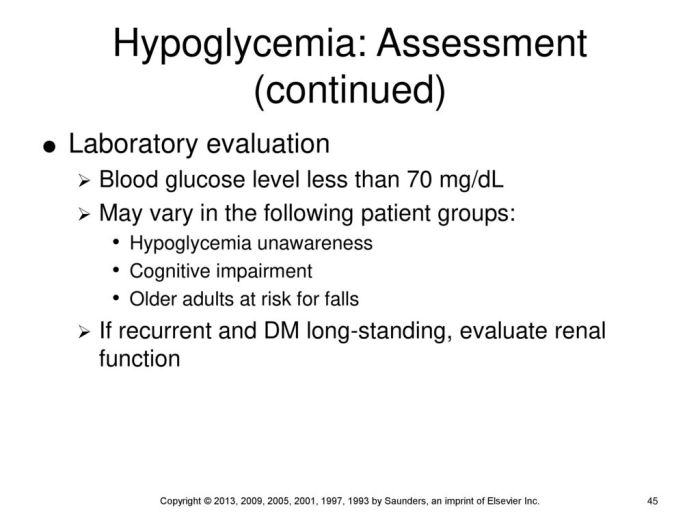
Typical blood glucose levels associated with hypoglycemia:* Less than 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L)Role of ketones in the diagnosis of hypoglycemia:* Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In hypoglycemia, ketones may be present in the urine or blood.
The presence of ketones suggests that the hypoglycemia is due to a lack of insulin, rather than an excess of insulin.
Other laboratory tests that may be helpful in evaluating hypoglycemia:* C-peptide: A hormone that is released with insulin. A low C-peptide level suggests that the hypoglycemia is due to a lack of insulin production.
Hemoglobin A1c
A measure of long-term blood glucose control. A high hemoglobin A1c level suggests that the hypoglycemia is due to poor blood glucose control.
History

Questions to ask patients about their symptoms of hypoglycemia:* When did the symptoms start?
- How long do the symptoms last?
- What were you doing when the symptoms started?
- What have you eaten or drunk in the past few hours?
- Do you have any other medical conditions?
- Are you taking any medications?
Importance of identifying potential triggers for hypoglycemia:* Identifying potential triggers for hypoglycemia can help to prevent future episodes.
Common triggers include
Skipping meals
Exercising too much
Drinking alcohol
Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medications
Dietary habits and medications that can contribute to hypoglycemia:* Dietary habits that can contribute to hypoglycemia include eating too few carbohydrates or eating carbohydrates that are too quickly digested.
Medications that can contribute to hypoglycemia include insulin, sulfonylureas, and meglitinides.
Differential Diagnosis
Conditions that can cause symptoms similar to hypoglycemia:* Alcohol intoxication
- Drug overdose
- Sepsis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Pituitary insufficiency
Key differentiating features between hypoglycemia and these other conditions:* Hypoglycemia is usually associated with a blood glucose level of less than 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L).
- Alcohol intoxication is usually associated with a blood alcohol level of greater than 80 mg/dL (0.08%).
- Drug overdose can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the drug that was taken.
- Sepsis is usually associated with a fever, chills, and hypotension.
- Hyperthyroidism is usually associated with weight loss, increased heart rate, and sweating.
- Adrenal insufficiency is usually associated with fatigue, weakness, and weight loss.
- Pituitary insufficiency is usually associated with fatigue, weakness, and menstrual irregularities.
Importance of ruling out other potential causes of hypoglycemia:* It is important to rule out other potential causes of hypoglycemia, such as alcohol intoxication, drug overdose, sepsis, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and pituitary insufficiency, before making a diagnosis of hypoglycemia.
Management
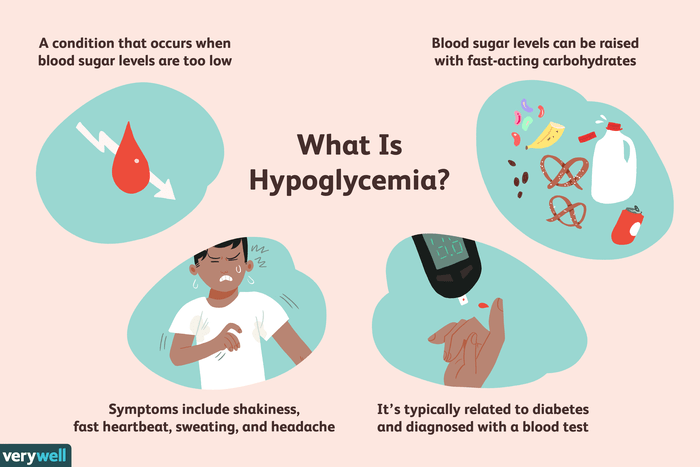
Initial steps to take when managing hypoglycemia:* Give the patient a fast-acting source of glucose, such as:
4 ounces of orange juice
15 grams of glucose gel
- 6 lifesavers
- Check the patient’s blood glucose level after 15 minutes.
- If the patient’s blood glucose level is still low, give another dose of glucose.
Different methods for administering glucose to patients with hypoglycemia:* Oral: The most common method of administering glucose is by mouth.
Intravenous (IV)
IV glucose is used when the patient is unable to take glucose by mouth.
Intramuscular (IM)
IM glucose is used when the patient is unable to take glucose by mouth or IV.Importance of monitoring patients after treatment for hypoglycemia:* Patients should be monitored after treatment for hypoglycemia to ensure that their blood glucose level does not drop too low again.
Patients should be instructed to eat a meal or snack within 30 minutes of treating hypoglycemia.
User Queries
What are the common physical signs of hypoglycemia?
Sweating, tremors, palpitations, hunger, and confusion are common physical signs of hypoglycemia.
What laboratory test is most commonly used to diagnose hypoglycemia?
A blood glucose test is the most commonly used laboratory test to diagnose hypoglycemia.
What are some potential triggers for hypoglycemia?
Missed meals, excessive exercise, and certain medications can be potential triggers for hypoglycemia.