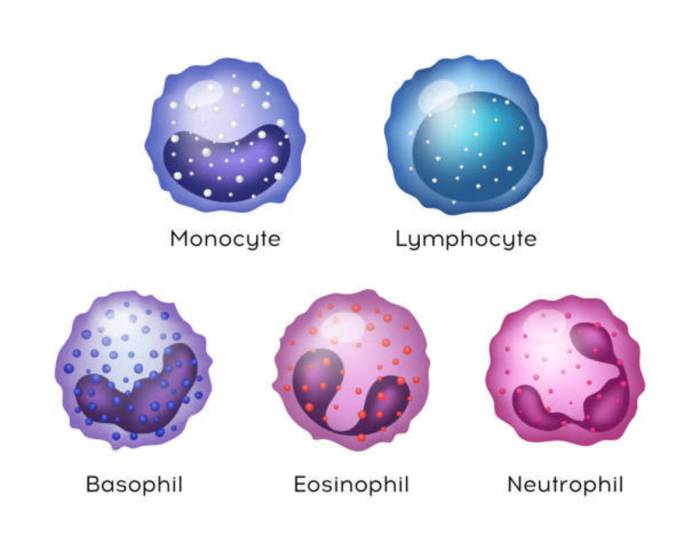
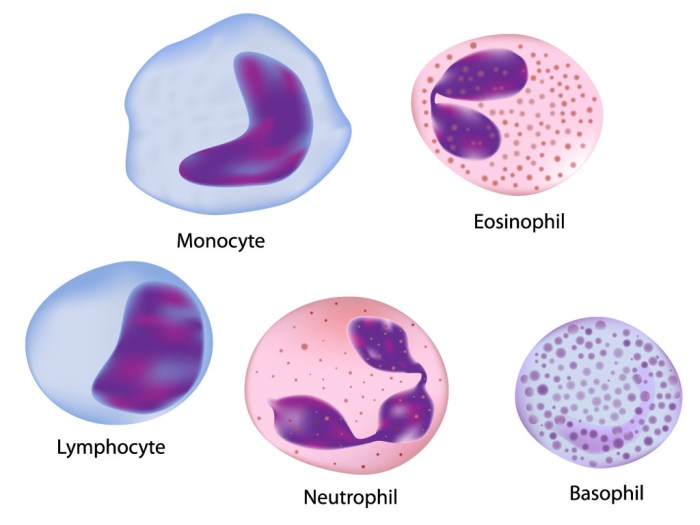
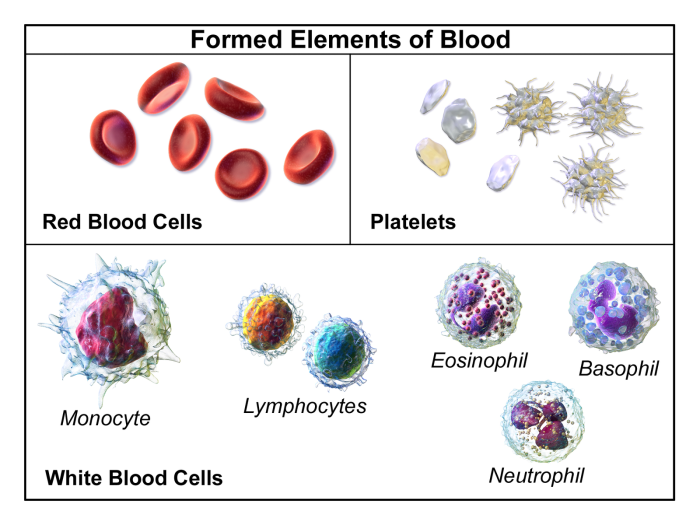
Four leukocytes are diagrammed in figure 10-2, setting the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the intricacies of neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes, unraveling their distinct functions, structures, and pivotal roles within the immune system.
Neutrophils, the most abundant leukocytes, serve as the body’s first line of defense against invading pathogens. Their multifaceted structure, including a multi-lobed nucleus and specialized granules, equips them to phagocytize and destroy foreign invaders. Eosinophils, known for their role in allergic reactions, possess a bilobed nucleus and eosinophilic granules that release cytotoxic mediators to combat parasitic infections.
Four Leukocytes
Leukocytes, also known as white blood cells, are essential components of the immune system. They play a vital role in protecting the body from infection and disease. There are four main types of leukocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes.
Neutrophil
- Primary function:Neutrophils are the most abundant type of leukocyte. They are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy bacteria and other foreign particles.
- Structure:Neutrophils are characterized by their multi-lobed nucleus and cytoplasmic granules.
- Role in the immune response:Neutrophils are the first responders to infection. They are rapidly recruited to the site of infection, where they phagocytose and kill invading pathogens.
Eosinophil
- Primary function:Eosinophils are involved in the defense against parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
- Structure:Eosinophils have a bilobed nucleus and cytoplasmic granules that contain eosinophilic proteins.
- Role in the immune response:Eosinophils release cytotoxic substances that kill parasites and degranulate to release inflammatory mediators that contribute to allergic reactions.
Basophil, Four leukocytes are diagrammed in figure 10-2
- Primary function:Basophils are involved in inflammation and allergic reactions.
- Structure:Basophils have a bilobed nucleus and cytoplasmic granules that contain histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
- Role in the immune response:Basophils release histamine and other inflammatory mediators that promote vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, leading to inflammation.
Lymphocyte
- Primary function:Lymphocytes are responsible for the adaptive immune response.
- Structure:Lymphocytes have a large, round nucleus and a small amount of cytoplasm.
- Role in the immune response:Lymphocytes recognize and bind to specific antigens, and then proliferate and differentiate into effector cells that can kill infected cells or produce antibodies.
Comparison of the Four Leukocytes
| Characteristic | Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Basophil | Lymphocyte |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Phagocytosis | Defense against parasites and allergic reactions | Inflammation and allergic reactions | Adaptive immune response |
| Structure | Multi-lobed nucleus, cytoplasmic granules | Bilobed nucleus, eosinophilic granules | Bilobed nucleus, histamine-containing granules | Large, round nucleus, small cytoplasm |
| Role in the immune response | First responders to infection | Defense against parasites and allergic reactions | Inflammation and allergic reactions | Recognition and killing of infected cells, antibody production |
Q&A: Four Leukocytes Are Diagrammed In Figure 10-2
What is the primary function of neutrophils?
Neutrophils are phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy invading pathogens, acting as the body’s first line of defense.
How do eosinophils contribute to allergic reactions?
Eosinophils release cytotoxic mediators from their eosinophilic granules, which help combat parasitic infections and contribute to the inflammatory response in allergic reactions.
What is the role of basophils in inflammation?
Basophils release histamine and other inflammatory mediators, which promote vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, contributing to the inflammatory response.
How do lymphocytes differ from other leukocytes?
Lymphocytes are unique in their ability to recognize and respond to specific antigens, playing a central role in the adaptive immune response.